Tool calling in Editor
Humanloop’s Prompt Editor supports tool calling functionality, enabling models to interact with external systems. This feature, equivalent to OpenAI’s function calling or Anthropic’s tool use, is implemented through JSON Schema Tools in Humanloop. These Tools adhere to the widely-used JSON Schema syntax, providing a standardized way to define data structures.
Within the Editor, you can create inline JSON Schema Tools as part of your Prompt. This capability allows you to establish a structured framework for the model’s responses, enhancing control and predictability.
Prerequisites
- You already have a Prompt — if not, please follow our Prompt creation guide first.
Create an inline JSON Schema Tool
Select a model that supports Tool Calling
Models supporting Tool Calling
To view the list of models that support Tool calling, see the Models page.
In the Editor, you’ll see an option to select the model. Choose a model like gpt-4.1-nano which supports Tool Calling.
Define the Tool
To get started with creating an inline tool, let’s use one of our preloaded examples.
Click on the + Tool button in the bottom left of the Editor. Select New inline tool….
In the modal that appears, open the Examples dropdown and select the get_current_weather tool.
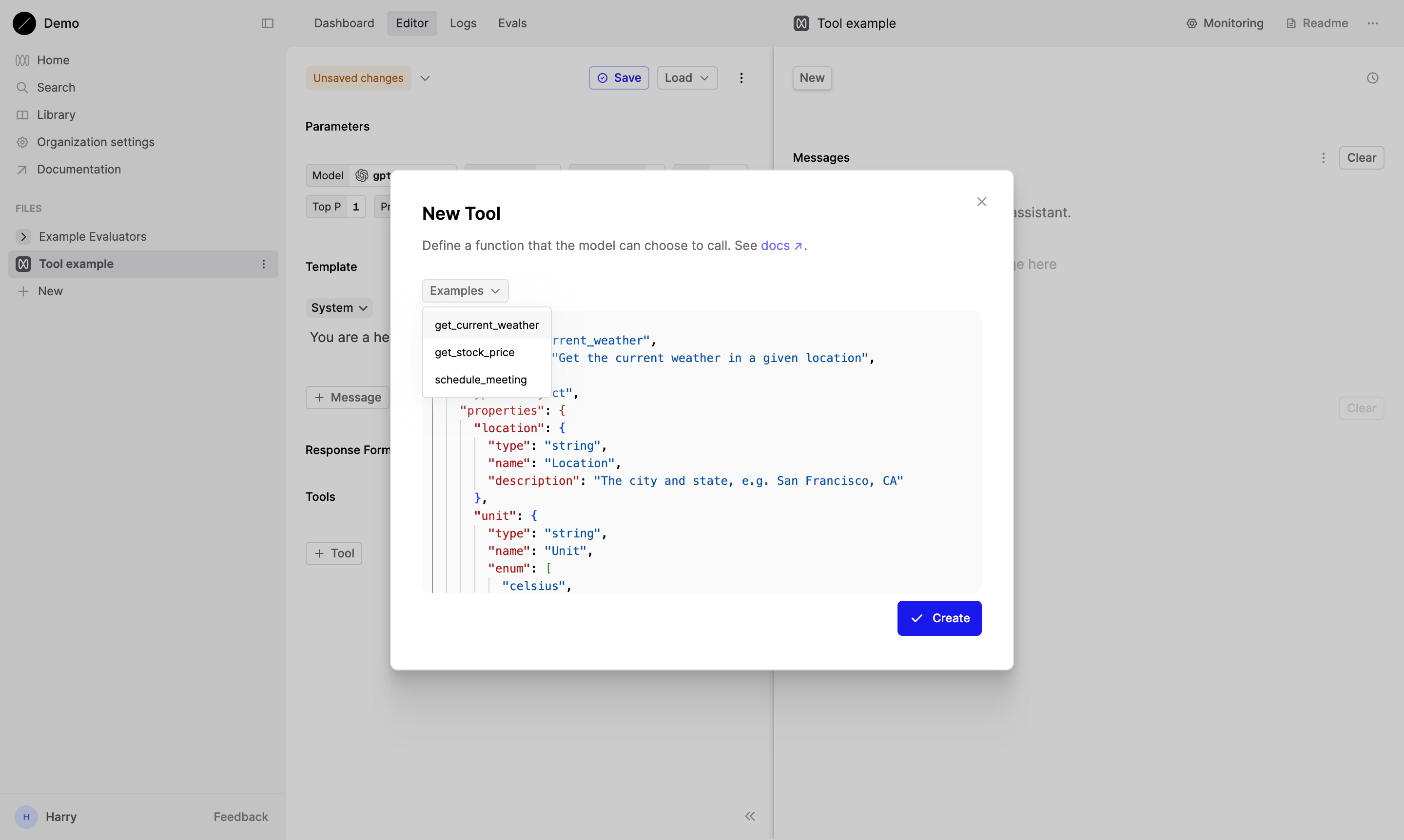
If you choose to edit or create your own tool, you’ll need to use the JSON Schema syntax. When creating a custom tool, it should correspond to a function you have defined in your own code. The JSON Schema you define here specifies the parameters and structure you want the AI model to use when interacting with your function.
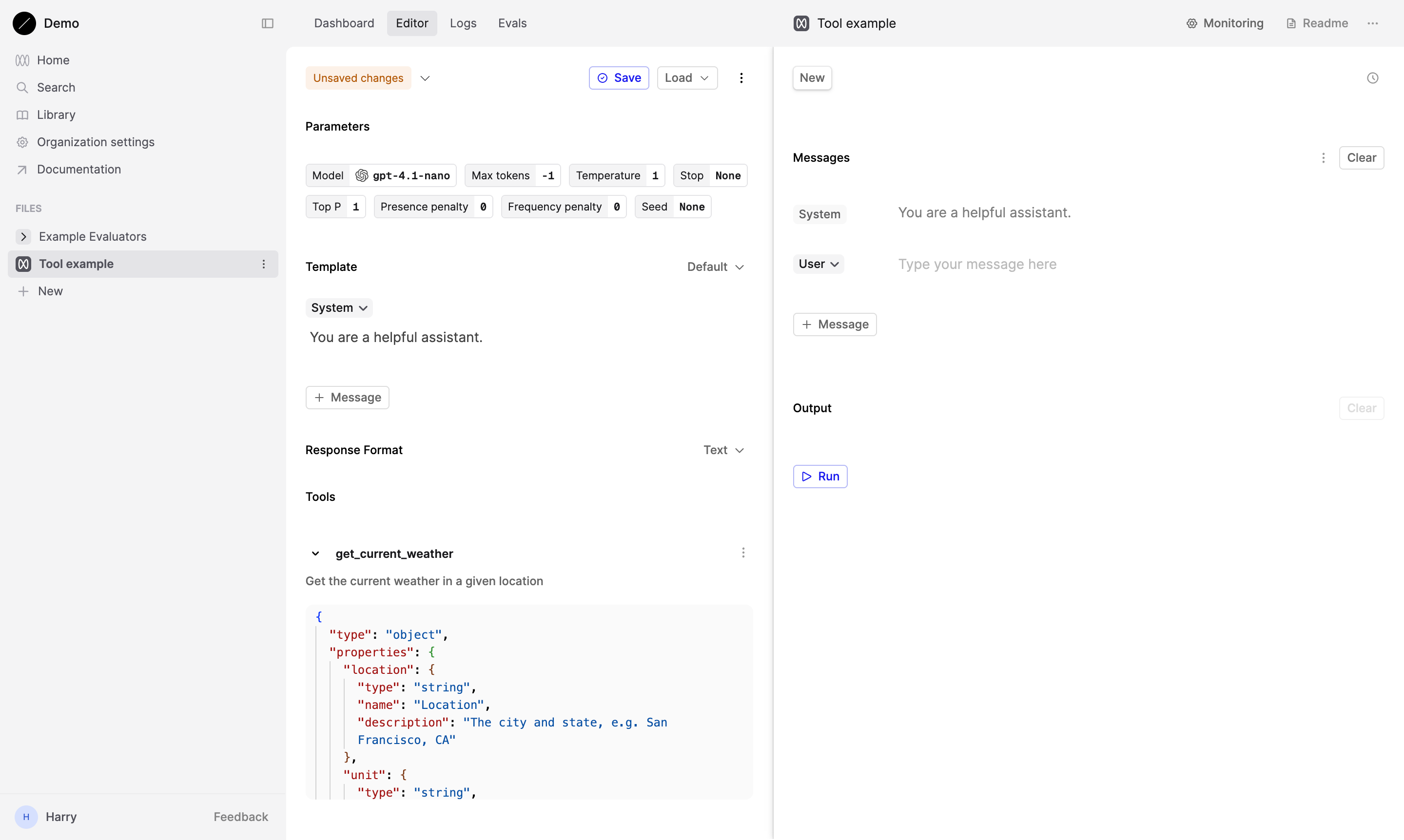
Test the Tool
Now, let’s test our Tool by inputting a relevant query. Since we’re working with a weather-related tool, try typing: “What’s the weather in Boston?” This should prompt the model to respond using the parameters we’ve defined.
Tool calling is context-sensitive
Keep in mind that the model’s use of the tool depends on the relevance of the user’s input. For instance, a question like ‘How are you today?’ is unlikely to trigger a weather-related tool call.
Check tool call
Upon successful setup, the assistant should respond by invoking the tool, providing both the tool’s name and the required data.
For our get_current_weather tool, the response might look like this:
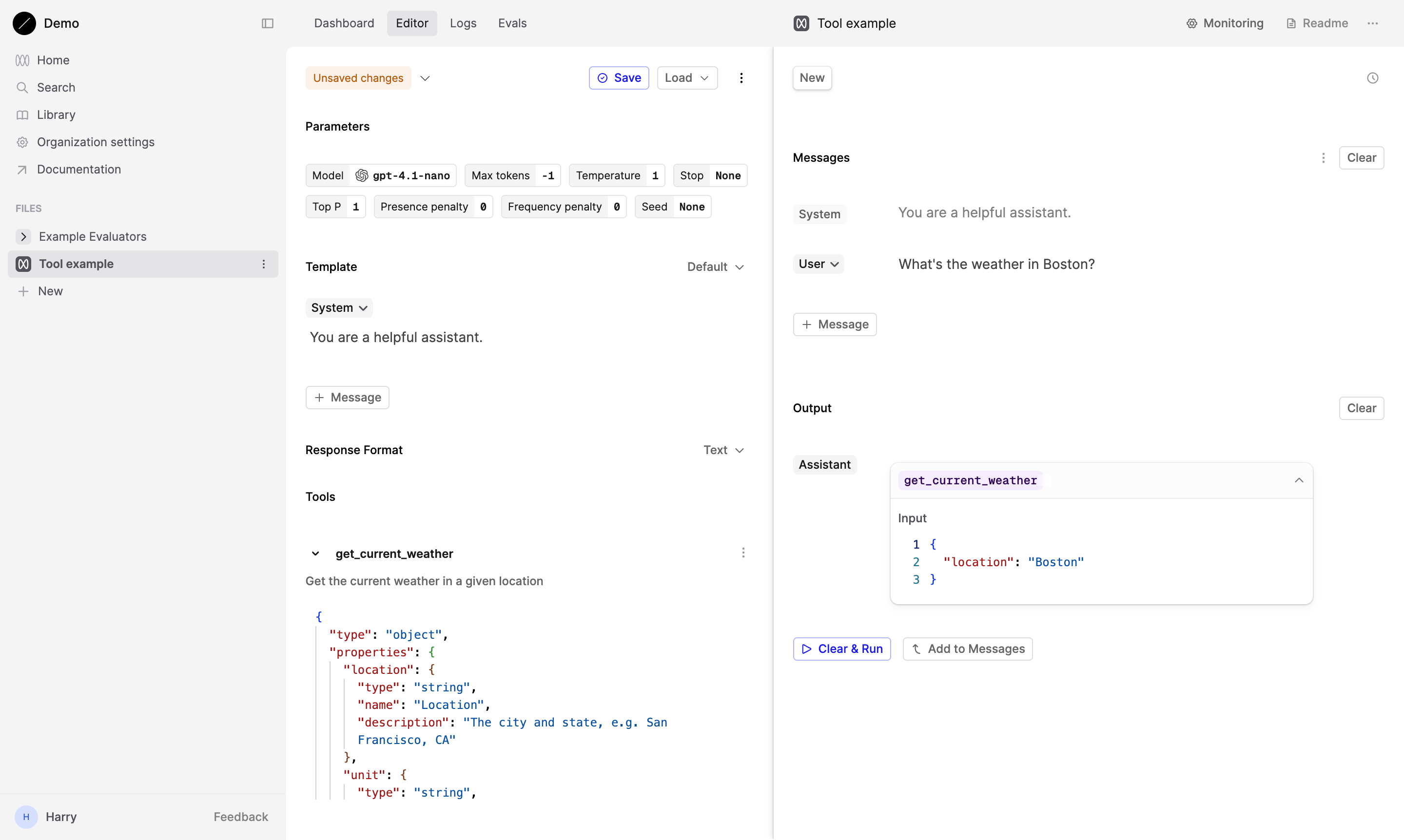
Submit tool response
You can also check how the Prompt would respond to a successful tool call.
Click on the Add to Messages button to move the assistant’s response into the Messages section for a subsequent call.
Then, you can paste in the exact response that the Tool would respond with into the Output section of the Tool call. For prototyping purposes, you can also just simulate the response yourself. Provide in a mock response:
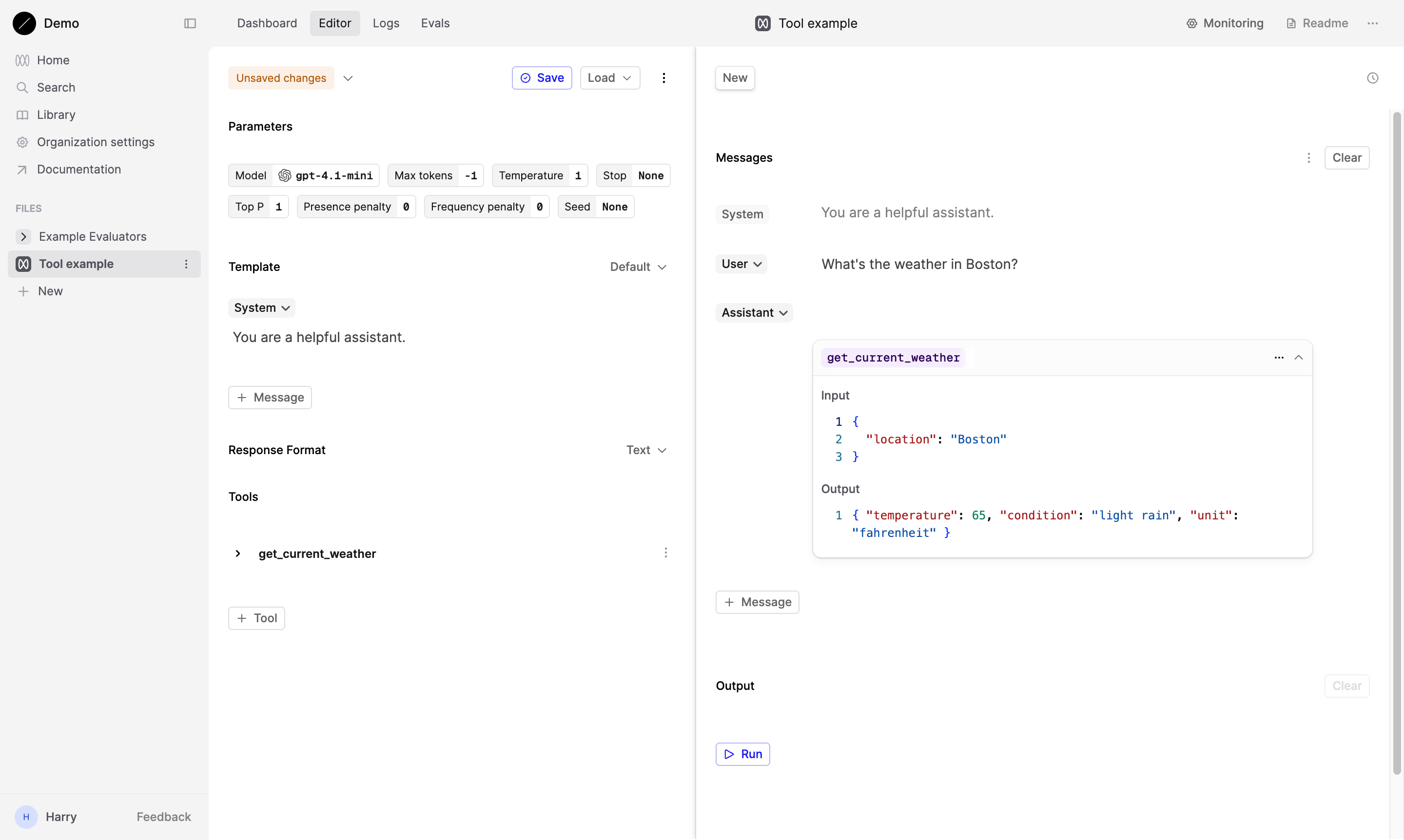
Remember, the goal is to simulate the tool’s output as if it were actually fetching real-time weather data. This allows you to test and refine your prompt and tool interaction without needing to implement the actual weather API.
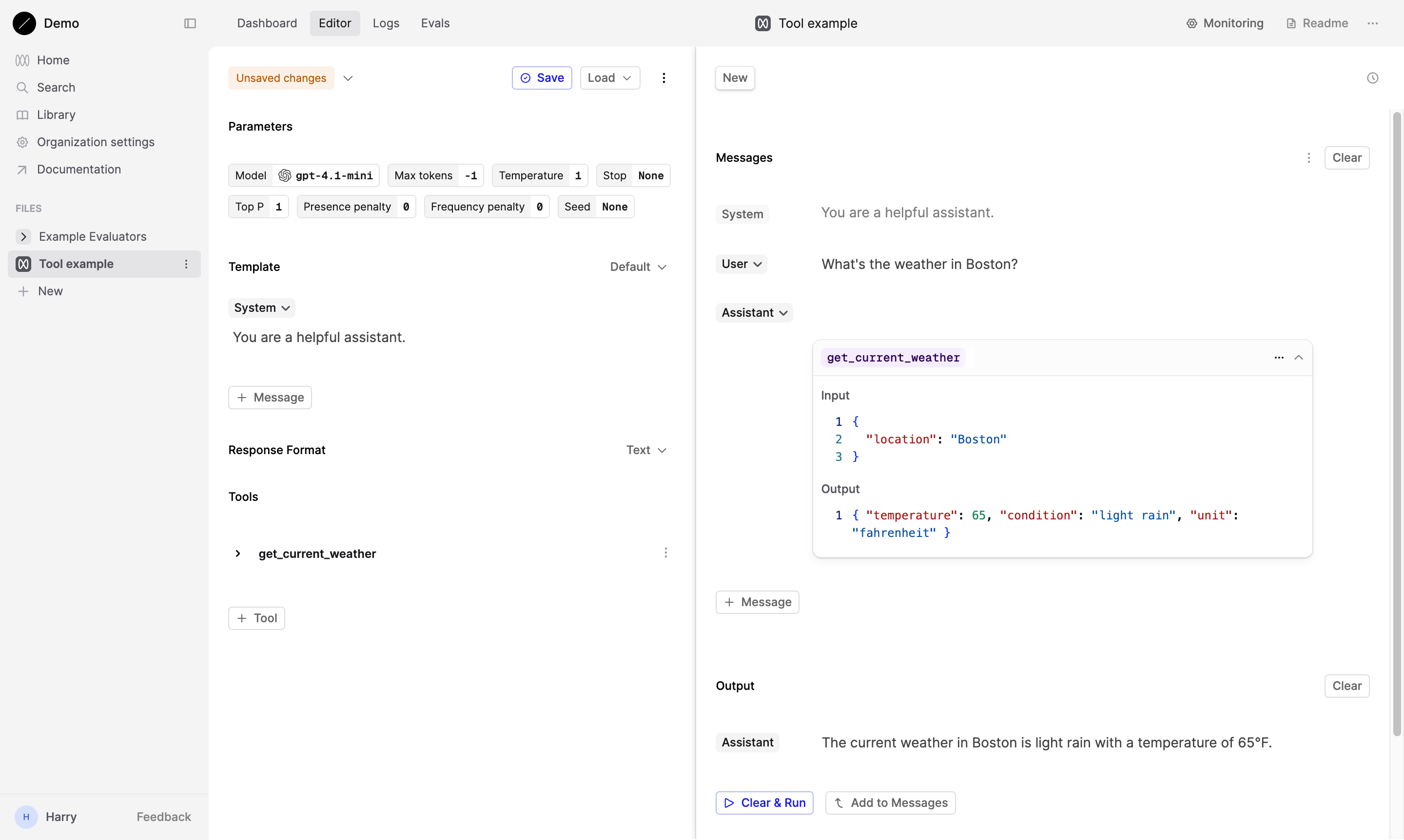
After entering the simulated tool response, click on the Run button to send the Tool’s response to the AI model.
Review assistant response
The assistant should now respond using the information provided in your simulated tool response. For example, if you input that the weather in Boston was 65°F and light rain, the assistant might say:
The current weather in Boston is light rain with a temperature of 65°F.
This response demonstrates how the AI model incorporates the tool’s output into its reply, providing a more contextual and data-driven answer.
Iterate and refine
Feel free to experiment with different queries. This iterative process helps you fine-tune your Prompt and understand how the AI model interacts with the tool, ultimately leading to more effective and accurate responses in your application.
Save your Prompt
By saving your Prompt, you will create a new version that includes the inline tool.
Congratulations! You’ve successfully learned how to use tool calling in the Humanloop Editor. This powerful feature allows you to test tool interactions, helping you create more dynamic and context-aware AI applications.
Next steps
After you’ve created and tested your inline Tool, you might want to reuse it across multiple Prompts. Humanloop allows you to link a Tool, making it easier to share and manage Tool definitions across multiple Prompts.
For more detailed instructions on how to link and manage Tools, check out our guide on Linking a JSON Schema Tool.