Logging through API
Our SDK offers high-level utilities for integrating Humanloop in your project. You can use the API to the same effect with any language you use or if you prefer more control.
This guide revisits our logging quickstart tutorial: we’ll use API actions instead of the SDK decorators, showing you how Humanloop instrumentation works step-by-step.
By the end, we’ll have a chat agent project integrated with Humanloop logging. The example uses the Python SDK, but the verbs map directly to our API.
Prerequisites
Account setup
Create a Humanloop Account
If you haven’t already, create an account or log in to Humanloop
Add an OpenAI API Key
If you’re the first person in your organization, you’ll need to add an API key to a model provider.
- Go to OpenAI and grab an API key.
- In Humanloop Organization Settings set up OpenAI as a model provider.
Using the Prompt Editor will use your OpenAI credits in the same way that the OpenAI playground does. Keep your API keys for Humanloop and the model providers private.
Install dependencies
Humanloop SDK requires Python 3.9 or higher. Optionally, create a virtual environment to keep dependencies tidy.
Create the chat agent
We start with a simple chat agent that answers math and science questions.
Python
TypeScript
Create an agent.py file and add the following:
Log to Humanloop
The agent works and is capable of function calling. However, we rely on inputs and outputs to reason about the behavior. Humanloop logging allows you to observe the steps taken by the agent, which we will demonstrate below.
Initialize the trace
Modify call_model to accept a trace_id argument. It will be used to associate Logs to the logging trace.
The trace of the conversation will be associated with a Flow. Initialize the trace at the start of the conversation.
Python
Typescript
Run the code
Have a conversation with the agent. When you’re done, type exit to close the program.
Python
TypeScript
Check your workspace
Navigate to your workspace to see the logged conversation.
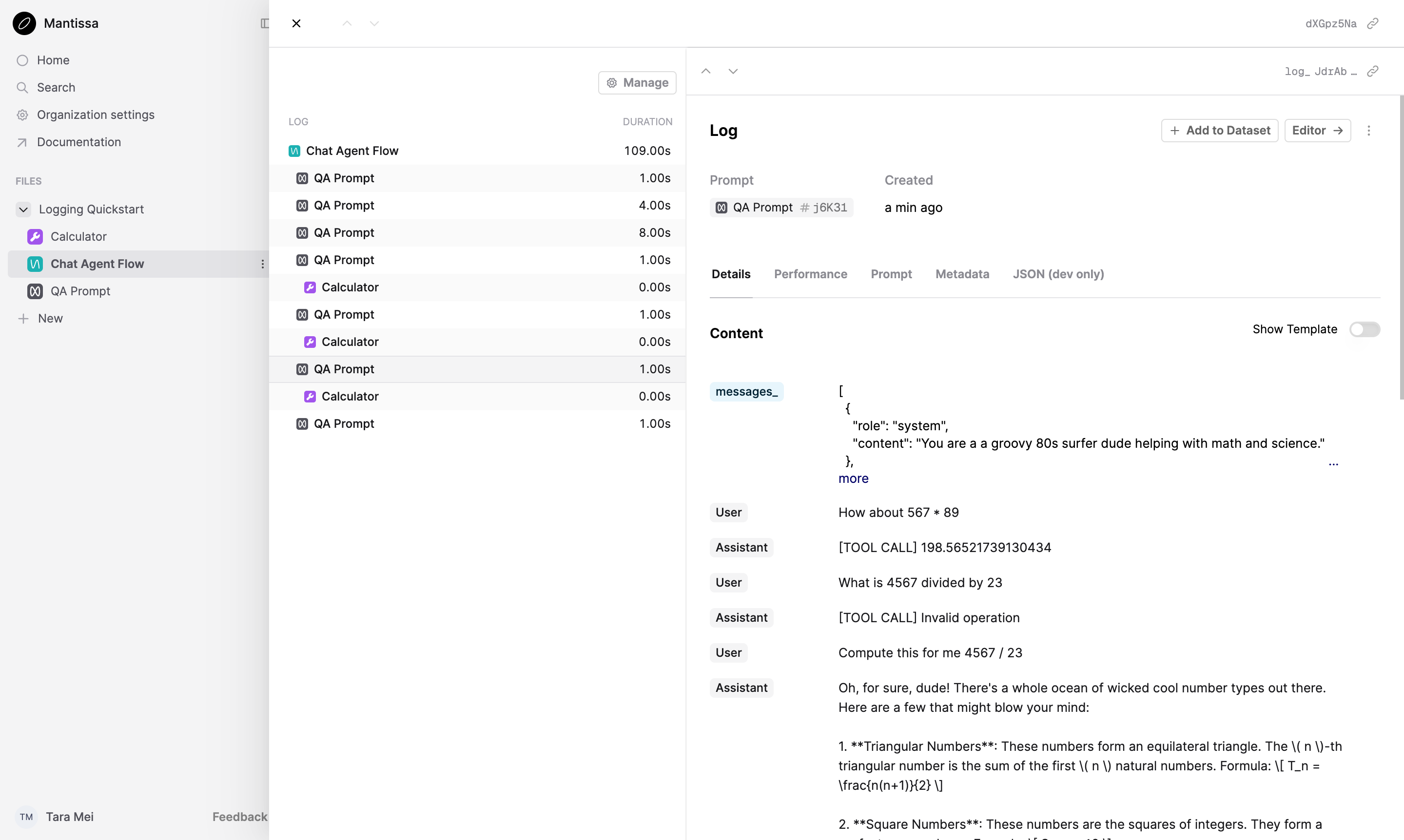
Inside the Logging Quickstart directory on the left, click the QA Agent Flow. Select the Logs tab from the top of the page and click the Log inside the table.
You will see the conversation’s trace, containing Logs corresponding to the Tool and the Prompt.
Change the agent and rerun
Modify the call_model function to use a different model and temperature.
Python
Typescript
Run the agent again, then head back to your workspace.
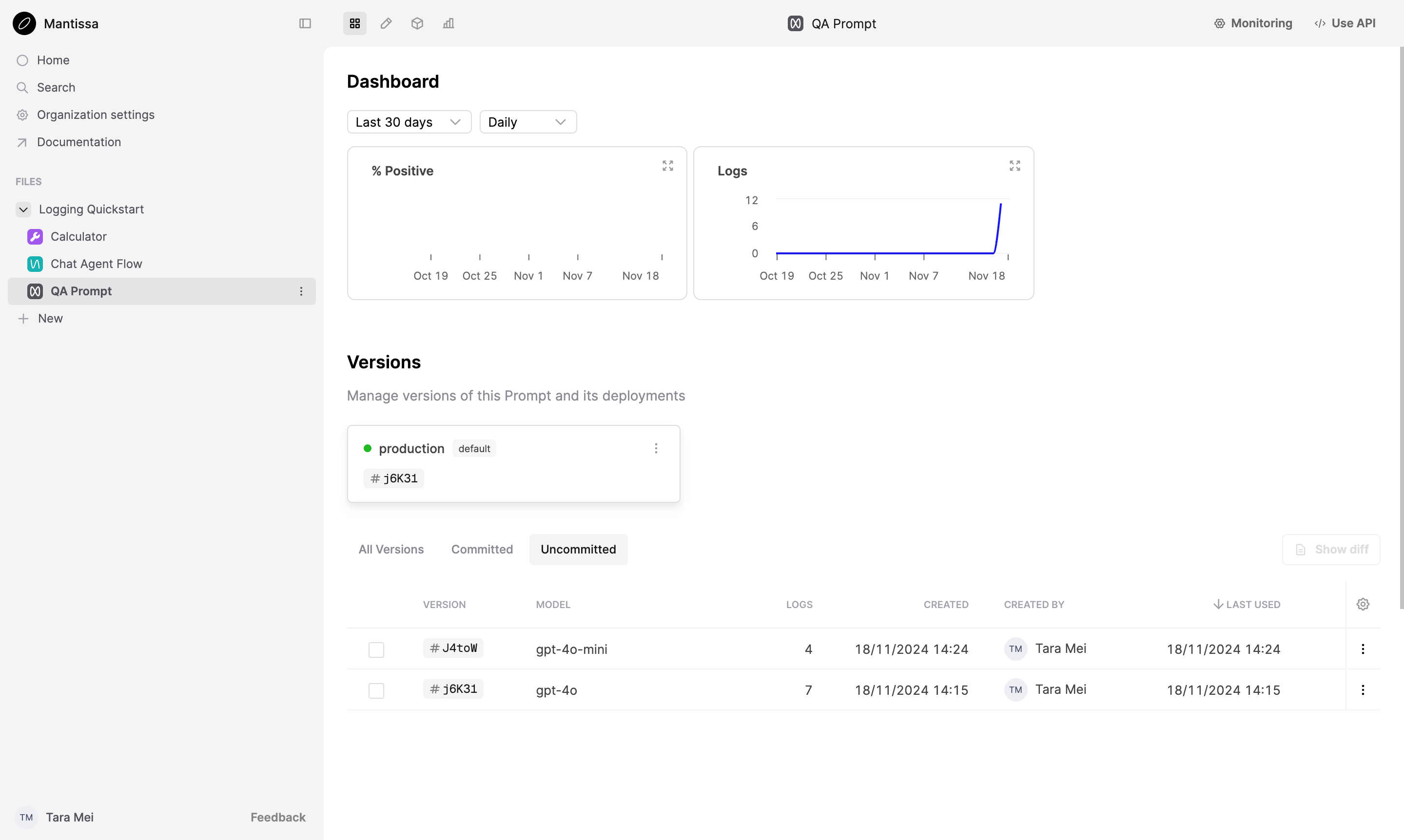
Click the QA Prompt Prompt, select the Dashboard tab from the top of the page and you should find a new version of the Prompt at the top of the list.
By changing the hyperparameters of the OpenAI call, you have tagged a new version of the Prompt.
Next steps
Logging is the first step to observing your AI product. Read these guides to learn more about evals on Humanloop:
-
Add monitoring Evaluators to evaluate Logs as they’re made against a File.
-
See evals in action in our tutorial on evaluating an agent.